[New Doone Big Data] Agricultural Big Data - Aid in Agricultural Safety
Release date: 2017-07-03 01:45:20
Poultry and vegetable are commonly consumed in our everyday life. Hence, are you concerned about the safety for consumption?
In recent years, excess in pesticide residues and presence of beta agonists (β-agonist) in our food has raised food-safety concerns, but this is merely the tip of the ice berg.
As such, there is an increase in food-safety concerns from consumers, and this means that an accurate tracking of the entire agricultural production process is essential.
New Doone leverages on QR code and RFID technology to provide thorough tracking on the entire agricultural production process. There will be seamless and up-to-date information exchange through utilisation of application by users (farms and companies) and support from relevant information systems. Companies utilising the system are able to grasp accurate information in the entire supply chain, and as such, have tighter control on food-safety. At the same time, other users simply have the scan the QR code to gain comprehensive food-safety related information on the respective food. The ability to trace back is essential for consumers and relevant firms to accurately identify the root of the problem and person responsible, in order for timely counter-measures.
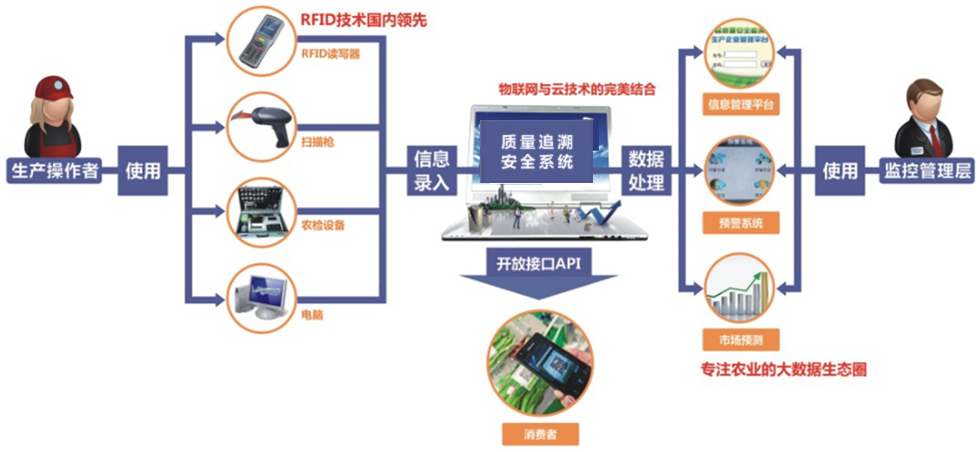
New Doone utilises our support system, application system, data management, storage system, safety system to streamline information flow with back-up systems, actual files – agricultural management, manufacturing information, safety-checks, and APP surveillance to gain extensive information regarding plantation, rearing process and all related fields.
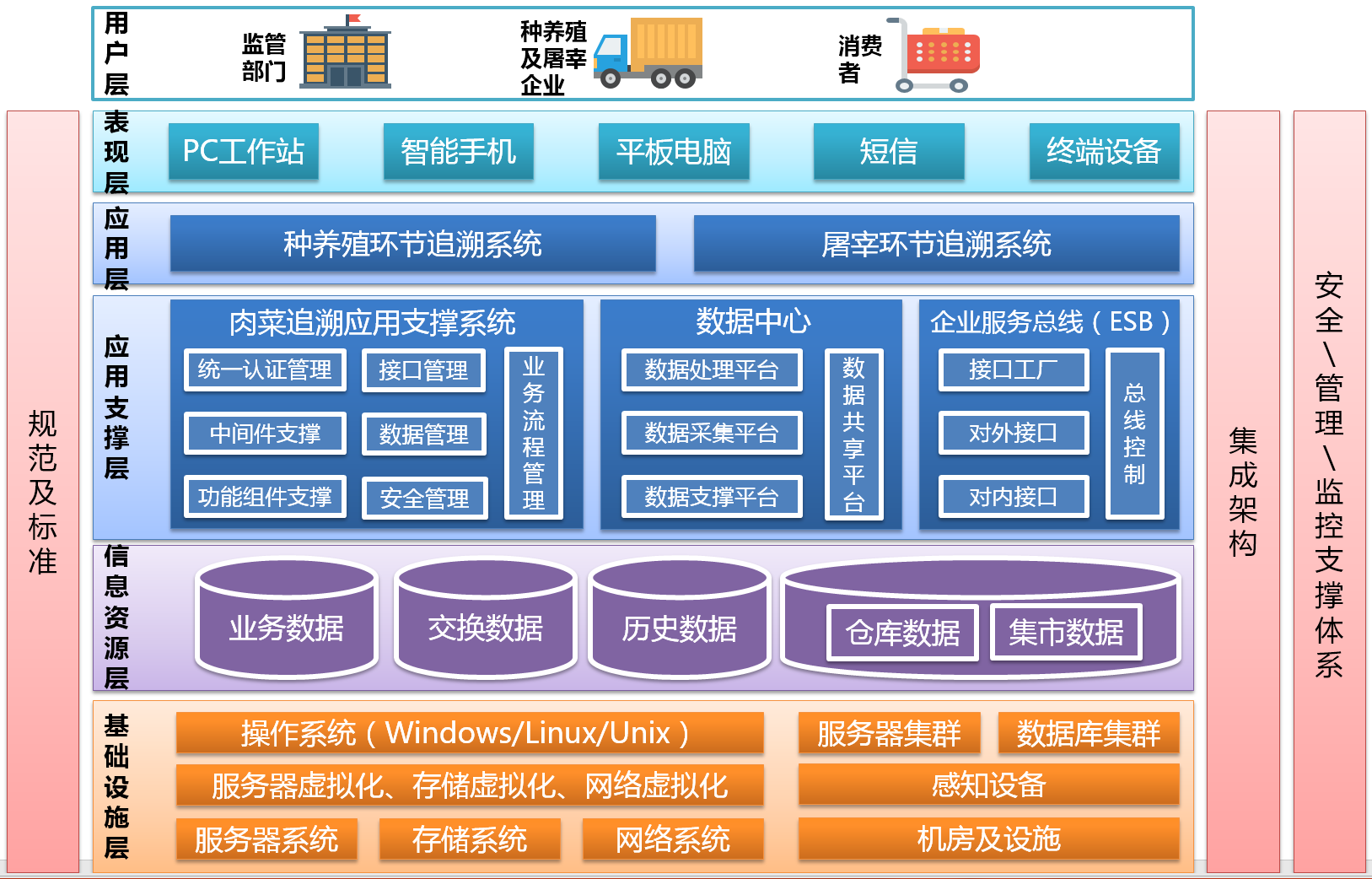
However, the uniqueness of our new system is not limited to mere tracking of processes, but a fully functional information system that provides comprehensive support for seamless information exchange in the entire supply chain.
Big Data’s role in accurate and precise management
Big Data is crucial in food-surveillance for food-safety. In the entire production process, there has to be strict surveillance on all aspect – surrounding environment, water source, soil, pesticide, fertiliser and relevant fields. In the past, one-sided data commonly led to inaccurate and micro-perspective of the entire occurring. Big Data provides comprehensive information and wholly representation of the entire situation, which provides accuracy when uncovering the truth. On the other hand, traditional agricultural management focuses mainly on larger areas of production, i.e. rice while neglecting smaller areas of productions, i.e. fruits and vegetables. Hence, most producers may simply abstract information from larger areas of production to derive final conclusions, which in turn compromises accuracy. With Big Data, such inaccuracy will be reduced or even omitted due to the comprehensive and accurate consolidation of data, for precise forecasts and evaluation of food-safety.
Big Data’s role in removing risks for consumers
Agricultural production consists of environmental, social and economic factors. From production to consumption, there are many processes such as plantation, marketing and retailing, of which any of them could possibly lead to a compromise in food-safety. Hence, the utilisation of Big Data allows strict surveillance and up-to-date data collection for precise evaluation. This aids greatly in lowering risks for consumers.
Big Data’s role in agricultural production
Sometimes, farms may choose products that are not suitable. For example, in the pesticide industry, there are many loopholes and incompatibility in systems. Currently, there are many types of pesticides in the market with different standards and of which, many are prohibited due to possible damage to crops. Therefore, we can make use of Big Data to keep track of environmental factors – including soil, water source and even pesticides for comprehensive surveillance. Following, the related departments could look into these data collected to identify the root of any problem for timely corrective measures. This reduces the risks surfaced and provides better quality assurance in food-safety.
Big Data’s role in food-transportation
With an increase in living standards for consumes, there is a greater demand for larger varieties in food. In order to meet the demand, it is crucial to have timely food-transportation. The perishable nature of agricultural products implies that any delay or inadequacy in transportation will greatly affect its quality. Thus, to maintain its quality, we can utilise Big Data to monitor the temperature, humidity and light during transportation to optimise changes. Big Data also helps to locate unethical producers who adds prohibited pesticides. Furthermore, we could even use Big Data GPS to track and locate the transportation vehicles in order to derive the fastest route to ensure that products are delivered at the quickest time possible.
Big Data’s role in retailing and sales
For sale of agricultural products, there has yet to be strict and relevant regulations. Due to the low barriers to entry, many unethical producers will make use of pesticides and preservatives that cannot be easily discovered by consumers. Once suspected, producers could easily shirk their responsibilities through the various loopholes. Hence, Big Data comes into play due to its ability in providing comprehensive information – including place of production, production data, production process, transportation and retailing. Through the leverage on Big Data, all products have their unique ID and QR code that cannot be compromised. This greatly limits the presence of blacklisted producers, reducing risks incurred. At the same time, consumers could also use the unique ID and QR code to trace back on the entire production for a greater assurance of mind during consumption.
Big Data’s role in food-safety and possible challenges
In the era of Big Data, Hazard analysis and critical control points (HACCP) is a systematic preventive approach to food safety from biological, chemical, and physical hazards in production processes that can cause the finished product to be unsafe, and designs measurements to reduce these risks to a safe level. Regular checks and changes ensures the top-notch quality of these products, which in turns increases assurance for the health of consumers. For example, Chu Cheng (储橙) has strict regulatory standards for their oranges. Their optimal 24:1 sweetness to sour ratio is a huge selling point that has successfully drawn a critical mass of consumers, which as a result, has also marked up the prices of their oranges. This is a great example of the positive effect in strict regulation for agricultural products. Xinjiang’s Red Dates and grapes have also gained a reputable name for themselves due to their well-known strict regulations on their products.
The country requires industry-standardised regulations to be implemented in order to assurance the quality of products. Currently, Apache™ Hadoop® is a framework that allows for the distributed processing of large data sets across clusters of computers using simple programming models. This has inspired us to produce a new information system that provides streamlined process of labelling, transmission, storage and management of information from collection of data to food-surveillance. As such, this increases the efficiency of information utilisation in Big Data which is vital in agricultural-safety.
Consolidation of all information hubs for greater synergies
For maximum utilisation of information, it is important to have thorough exchange of information. On one hand, agricultural production consists of various environmental, social and political factors which leads to restricted and limited information exchange. On the other hand, there is still negligence for governmental-implemented regulations. In the Big Data era, the lack of information results in under-utilisation of possible resources. A mutual industry-standardised platform is bound to provide seamless flow of information between all relevant departments in the agricultural production process. An efficient flow of information between all is bound to improve the efficiency and standards of food-safety and in turn, creates great synergies. The relevant departments need to make use of all possible social media platforms and communication sources i.e. newspapers, television, Weibo, social media platforms to actively share up-to-date news to assure and build greater trust in consumers.
For example, the Chinese television series ‘A Bite of China’ was successful in sharing agricultural-related information with the public. The well-received television series was a huge contributing factor to the increase in sales of Nuodeng Ham and other related products. This has provided a new platform for sharing of agricultural-information for the creation of new photos and videos have drawn the attention and interest of audience, which has spurred on the involvement of consumers in food-safety.

